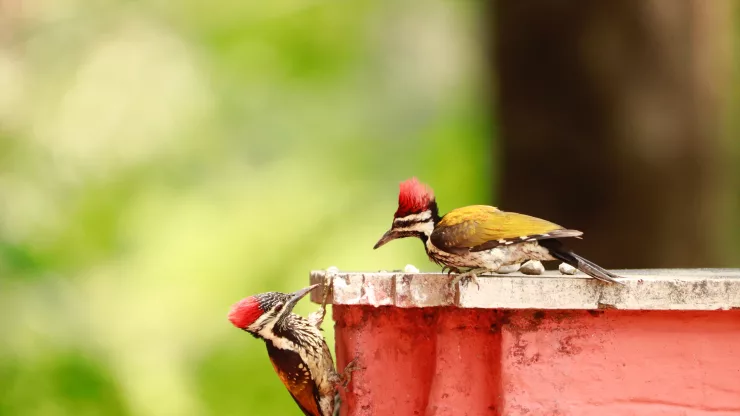
Woodpeckers are fascinating birds that are known for their ability to peck at trees with their sharp beaks.
They are found in many different habitats, from dense forests to urban areas.
In this article, we will explore the urban woodpecker’s diet and why studying it is important for conservation efforts.
Jump to Section
Introduction
Woodpeckers are a group of birds that are known for their unique ability to peck at trees with their sharp beaks.
They are found in many different habitats, from dense forests to urban areas.
In this article, we will explore the urban woodpecker’s diet and why studying it is important for conservation efforts.
Why study the urban woodpecker’s diet?
Studying the urban woodpecker’s diet can provide valuable insights into the impact of urbanization on wildlife.
As cities continue to expand, natural habitats are being destroyed, and many species are struggling to survive.
By studying the urban woodpecker’s diet, we can gain a better understanding of how these birds are adapting to urban environments and what we can do to protect them.
The Ecological Role of Woodpeckers
Woodpeckers play an important ecological role in forest ecosystems. They are known for their ability to excavate cavities in trees, which provides nesting sites for other bird species.
Additionally, their pecking activity can have a significant impact on the health of trees and the diversity of other species in the ecosystem.
Woodpecker’s impact on forest ecosystems
Woodpeckers are considered keystone species in many forest ecosystems.
They play an important role in maintaining tree health by removing diseased and dead wood, which can help reduce the spread of tree diseases.
Additionally, their pecking activity can create openings in trees, which can provide habitat for other bird species and increase the overall diversity of the ecosystem.
The benefits of woodpecker activity for other species
The cavities created by woodpeckers can provide valuable nesting sites for other bird species, such as chickadees, nuthatches, and bluebirds.
Additionally, the insects that are attracted to the sap and rotting wood in the cavities can provide a food source for other species, such as bats and small mammals.
Urbanization and the Woodpecker’s Diet
As more natural habitats are destroyed by urbanization, many species are forced to adapt to urban environments in order to survive.
For woodpeckers, this means finding new sources of food and nesting sites in urban areas.
How urbanization affects woodpeckers
Urbanization can have a significant impact on woodpecker populations.
As trees are removed to make way for buildings and roads, the birds may struggle to find suitable nesting sites and food sources.
Additionally, the noise and disturbance associated with urban areas can make it difficult for woodpeckers to communicate with each other and attract mates.
What do urban woodpeckers eat?
Urban woodpeckers have a diverse diet that includes insects, seeds and nuts, and berries and fruits.
Insects
Insects are a staple of the woodpecker’s diet, and urban woodpeckers are no exception.
They often feed on insects that are found in dead or dying trees, as well as insects that are attracted to sap and rotting wood.
Seeds and nuts
Urban woodpeckers also eat seeds and nuts, which can be found in parks and other green spaces in urban areas.
They may feed on acorns, beech nuts, and other types of nuts that are found in urban environments.
Berries and fruits
Berries and fruits are another important food source for urban woodpeckers.
They may feed on berries that are found in parks and other green spaces, as well as fruits that are found in urban gardens and orchards.
Researching Urban Woodpecker Diets
Studying the diets of urban woodpeckers can provide valuable insights into how these birds are adapting to urban environments and what we can do to protect them.
Techniques for studying woodpecker diets
Researchers can use a variety of techniques to study woodpecker diets, including analyzing their droppings and stomach contents, observing their feeding behavior, and using radio telemetry to track their movements.
Results from recent studies
Recent studies have shown that urban woodpeckers have a diet that is similar to that of their non-urban counterparts, but with some notable differences.
Comparison between urban and non-urban woodpecker diets
One study found that urban woodpeckers in Madrid, Spain, had a diet that was similar to that of their non-urban counterparts, but with a higher proportion of insects and a lower proportion of fruits and berries.
Seasonal variations in diet
Another study found that the diet of urban woodpeckers in the United States varied depending on the season.
In the summer, they primarily fed on insects, while in the winter, they fed on seeds and nuts.
Implications for urban planning and conservation efforts
Studying the diets of urban woodpeckers can have important implications for urban planning and conservation efforts.
By understanding what these birds are eating and how they are adapting to urban environments, we can make better decisions about how to manage and protect natural habitats in urban areas.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some other ways that urbanization can impact woodpecker populations?
In addition to destroying natural habitats, urbanization can also contribute to air and water pollution, which can have a negative impact on woodpecker populations.
Additionally, the noise and disturbance associated with urban areas can make it difficult for woodpeckers to communicate with each other and attract mates.
How can we protect woodpecker populations in urban areas?
To protect woodpecker populations in urban areas, we can create green spaces and wildlife corridors that provide suitable habitat and food sources.
Additionally, we can reduce pollution and noise levels in urban areas, which can help make it easier for woodpeckers to communicate and attract mates.
I’m a nature enthusiast and creator of Metro Wilds and have spent years exploring the great outdoors.
With a passion for environmental conservation and sustainability, I have dedicated my career to writing about the beauty and wonders of nature, as well as the threats facing our planet.
Contact me at [email protected] for assistance.